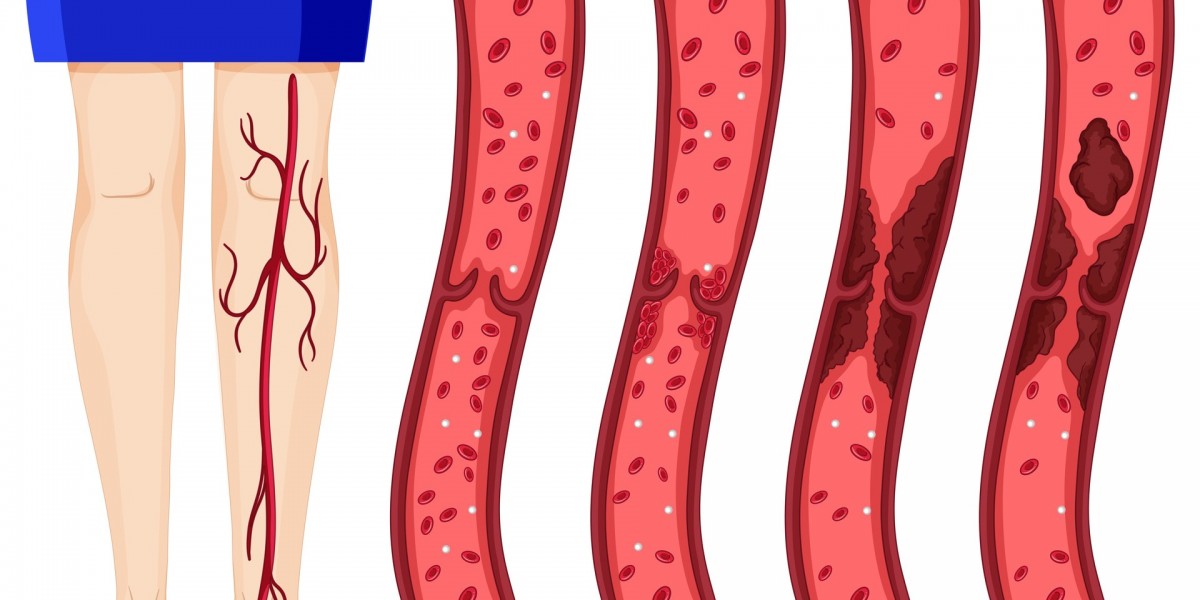
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the body, most often in the legs. While some cases may go unnoticed, untreated DVT can lead to dangerous complications, including pulmonary embolism, a condition that can be life-threatening.
The good news is that recognizing the common DVT symptoms you should never ignore can save lives. This article will guide you through the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options for DVT, all written in simple, human-like language so it’s easy to understand.
What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep Vein Thrombosis happens when a clot develops in the deep veins, often in the lower legs or thighs. Unlike superficial clots, DVT can block circulation, damage blood vessels, and even travel to the lungs.
Since DVT can develop silently, paying attention to early warning signs is crucial.
Common DVT Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
1. Leg Swelling
One of the most noticeable signs of DVT is swelling, usually in one leg. This swelling may appear suddenly and can feel tight or heavy.
2. Pain or Tenderness in the Leg
DVT pain is often compared to a cramp or soreness that doesn’t improve with rest. It may worsen when standing, walking, or flexing your foot.
3. Skin Discoloration
A leg affected by DVT might look red, bluish, or pale. This change in color happens because of poor blood flow.
4. Warmth Over the Affected Area
The skin in the area of the clot may feel noticeably warmer compared to the rest of the leg.
5. Heaviness or Fatigue in the Leg
Many patients report that their affected leg feels heavy or unusually tired, even without much physical activity.
6. Sudden Shortness of Breath (Serious Complication)
If the clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, it can cause sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate care.
What Causes DVT?
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of DVT:
Prolonged immobility – Sitting for long hours during travel or bed rest after surgery.
Surgery or trauma – Especially orthopedic surgeries involving the hips, legs, or pelvis.
Medical conditions – Heart disease, cancer, or clotting disorders.
Hormonal changes – Pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy.
Obesity – Excess body weight increases vein pressure.
Smoking – Damages blood vessels and increases clot risk.
Age – Risk increases with age, especially after 60.
Risk Factors for DVT
You are at higher risk of developing common DVT symptoms if you:
Have a family history of blood clots.
Lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Recently underwent major surgery.
Travel frequently on long-haul flights.
Have chronic illnesses such as diabetes or heart disease.
How to Prevent DVT
Preventing DVT is easier than treating its complications. Here are simple prevention strategies:
Stay active – Move around every 1–2 hours, especially during travel.
Exercise regularly – Walking, swimming, or yoga improves circulation.
Stay hydrated – Proper hydration prevents blood from thickening.
Wear compression stockings – Helpful for people prone to clotting or with vein issues.
Quit smoking – Improves vascular health and reduces clot risk.
Maintain a healthy weight – Reduces pressure on the veins.
How Is DVT Diagnosed?
If you experience any DVT symptoms you should never ignore, consult a healthcare provider immediately. Doctors may recommend:
Ultrasound – Detects clots in the veins.
Blood test (D-dimer) – Measures clotting activity.
Venography – X-ray with contrast dye to visualize clots.
MRI or CT scan – Used in complex cases.
Treatment Options for DVT
Treatment focuses on stopping clot growth, preventing new clots, and avoiding complications. Options include:
Blood thinners (anticoagulants) – Prevent new clots from forming.
Thrombolytic therapy – Breaks down clots quickly in severe cases.
Compression stockings – Reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
Surgical procedures – Rarely used, but may include filters to prevent clots from traveling to the lungs.
Living With DVT
Even after successful treatment, DVT can recur. Lifestyle adjustments play a huge role in long-term management:
Take prescribed medications regularly.
Attend follow-up appointments.
Monitor your legs for recurring swelling or pain.
Stay physically active to support healthy circulation.
Conclusion
Deep Vein Thrombosis is often called a “silent threat” because it can develop without noticeable symptoms until it becomes dangerous. Recognizing common DVT symptoms you should never ignore—such as swelling, leg pain, skin discoloration, and sudden shortness of breath—can be life-saving.
Early detection, medical treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices are key to preventing complications and maintaining good vascular health. If you ever suspect DVT, don’t wait—seek medical help immediately.
FAQs
1. What are the most common DVT symptoms?
The most common signs include leg swelling, pain, redness, warmth, and heaviness in one leg.
2. Can DVT be cured?
DVT can be treated effectively with medication and lifestyle changes, but it requires ongoing management to prevent recurrence.
3. How quickly do DVT symptoms appear?
Symptoms can develop gradually over days or appear suddenly, depending on clot size and location.
4. Can exercise prevent DVT?
Yes, regular exercise improves circulation and reduces the risk of clot formation.
5. What happens if DVT is left untreated?
Untreated DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal if not managed promptly.