Unlocking the Secrets of Analog Input Modules: Discover Their Essential Roles Across Industries!
In the realm of industrial automation and control systems, understanding the components that drive efficiency and accuracy is paramount. Among these components, analog input modules stand out as critical players. These modules serve as the bridge between the physical world and the digital realm, converting real-world signals into data that can be processed and analyzed. From monitoring temperature in manufacturing plants to gauging pressure levels in medical devices, the significance of analog input modules cannot be overstated. Whether you are an engineer, a technician, or simply someone intrigued by automation, grasping the intricacies of these modules is essential for navigating various industries where precision is key.
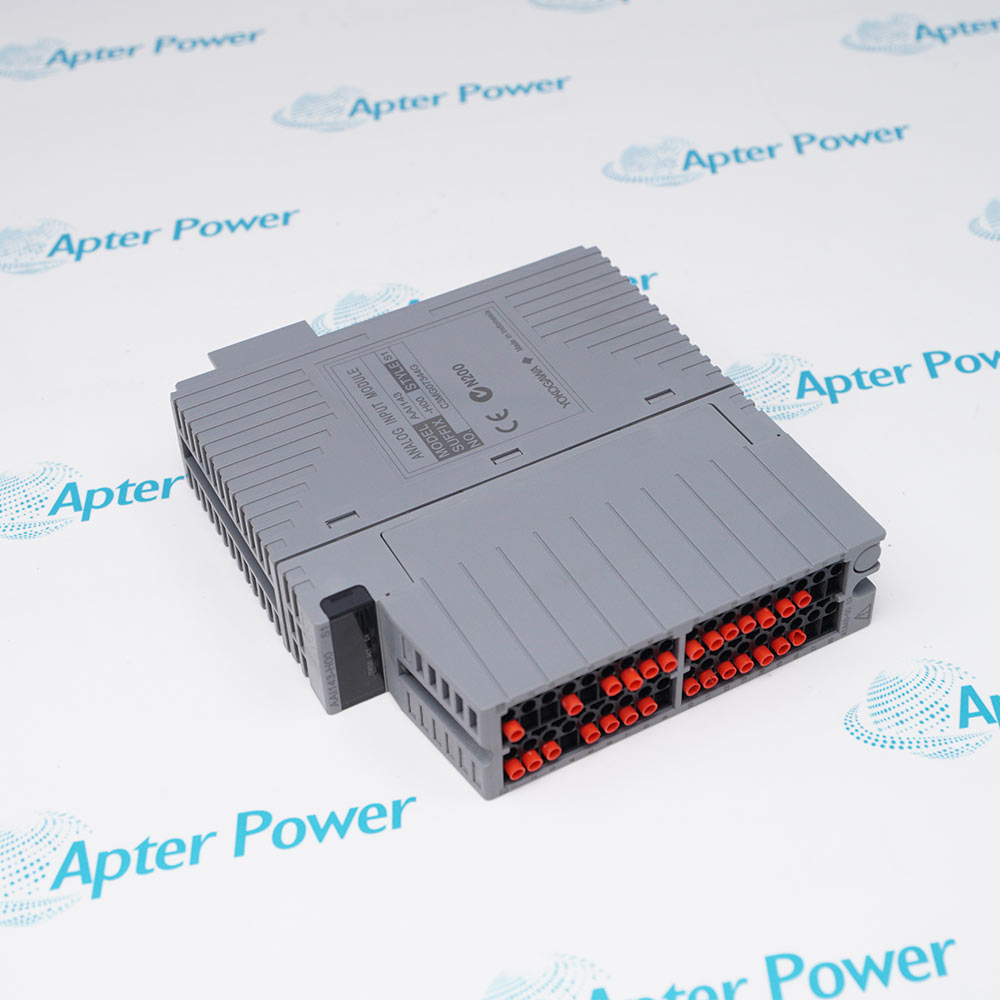

Understanding Analog Input Modules
An analog input module is a crucial component in control systems that processes signals from various sensors. Its primary function is to convert analog signals, such as voltage or current, into digital data that a computer or control system can interpret. This conversion is vital because most control systems operate on digital data. The basic components of an analog input module include signal conditioning circuits, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), and interfacing elements that connect the module to sensors. For instance, when measuring temperature with a thermocouple, the analog input module takes the tiny voltage produced by the thermocouple and uses the ADC to convert it into a digital signal. This digital representation can then be fed into a programmable logic controller (PLC) or a computer for further processing, analysis, and action. Understanding how these modules function is key for anyone working with automated systems, as they directly impact the reliability and accuracy of data collection.
Functions of Analog Input Modules
Analog input modules perform several essential functions that enhance the performance of automation systems. One of their primary roles is signal conditioning, which involves filtering and amplifying the raw signals received from sensors. This ensures that the data being processed is accurate and free from noise or interference. Additionally, these modules facilitate data acquisition by continuously sampling the input signals and converting them into a format that can be understood by the control system. This real-time data acquisition is crucial for applications requiring immediate feedback, such as in process control or safety monitoring. Furthermore, analog input modules interface with various types of sensors, including temperature sensors, pressure transducers, and flow meters. By effectively managing these interactions, analog input modules ensure seamless communication between physical devices and digital systems, ultimately contributing to a more efficient and responsive automation environment.
Applications Across Industries
Analog input modules find applications in a diverse range of industries, showcasing their versatility and importance. In the manufacturing sector, these modules are integral to process control systems, allowing for precise monitoring of variables like temperature, pressure, and flow rates. For instance, in an automotive assembly line, analog input modules can monitor the temperature of welding equipment, ensuring optimal conditions for production. In healthcare, they play a critical role in medical devices, such as patient monitoring systems where they convert signals from sensors measuring heart rate or blood pressure into digital data for analysis. Similarly, in energy management, these modules are used to track power consumption and optimize energy usage in smart grids. The benefits of using analog input modules in these contexts are manifold, including enhanced data accuracy, improved operational efficiency, and increased safety, making them indispensable to modern industry practices.
Future Trends in Analog Input Modules
As technology continues to evolve, so too do the capabilities and applications of analog input modules. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards greater integration with the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing for remote monitoring and control of systems on an unprecedented scale. Advancements in sensor technology are also paving the way for more sophisticated analog input modules that can handle a wider range of inputs and offer higher precision. Furthermore, the push for automation and smart manufacturing means that these modules will likely see increased demand as industries strive for greater efficiency and connectivity. Speculatively, the future may hold innovations such as advanced predictive analytics powered by real-time data from these modules, enabling proactive maintenance and operational improvements.
Significance of Analog Input Modules in Modern Systems
In summary, analog input modules are vital components in the world of automation and control systems, bridging the gap between analog signals and digital processing. Their ability to convert physical signals into actionable data underpins a vast array of applications across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and energy management. As we look toward the future, the continued advancement of these modules promises to enhance their capabilities and expand their applications even further. Understanding the functions and importance of analog input modules is essential for anyone involved in the fields of engineering and automation, as they play a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and reliability in modern industrial practices.