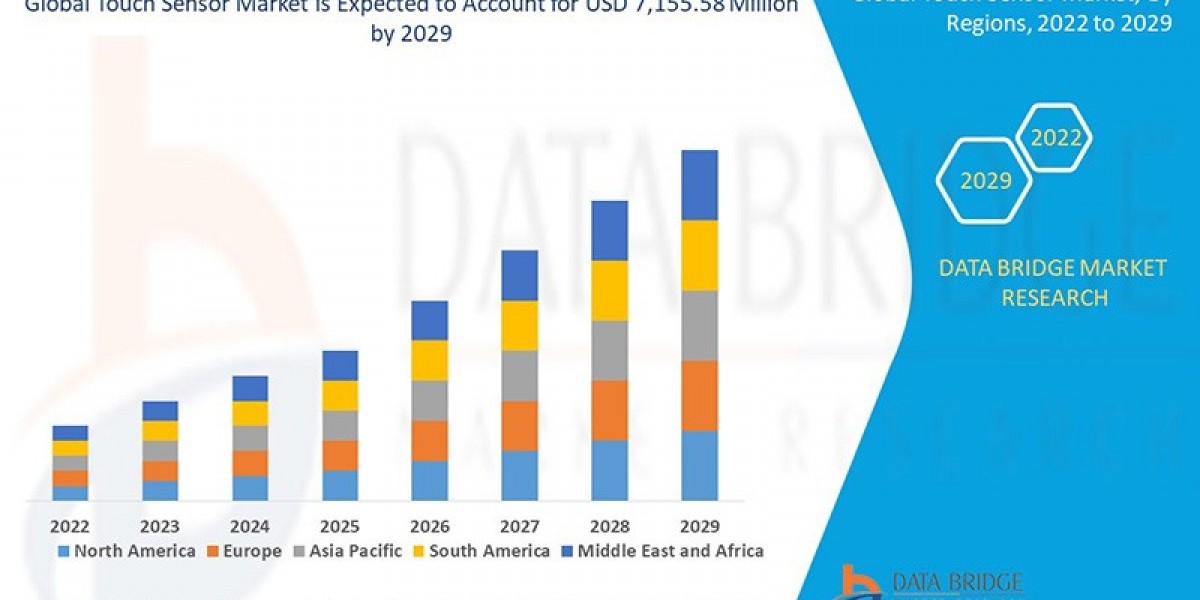
As digital devices become increasingly immersive and user-friendly, touch sensors have become the cornerstone of modern human-machine interfaces (HMIs). From smartphones and ATMs to industrial control panels and interactive displays, touch sensors enable intuitive interaction through gesture, tap, swipe, or press, eliminating the need for physical buttons or peripherals.
What is a Touch Sensor?
A touch sensor Market Share is an input device that detects and responds to physical contact (typically by a finger or stylus). It converts touch events into electrical signals, which are then interpreted by a microcontroller or computer to perform specific actions such as opening an app, scrolling content, or triggering commands.
Touch sensors are found in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, automotive systems, healthcare devices, and more.
Types of Touch Sensing Technologies
1. Capacitive Touch Sensors
Detect touch via changes in capacitance caused by a human finger.
Most widely used in smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Can support multi-touch and gesture recognition.
Works through glass or plastic covers.
2. Resistive Touch Sensors
Made of two conductive layers separated by a gap.
Touch pressure causes the layers to contact and register input.
Supports stylus and gloved input.
More affordable, but less durable and lower in clarity.
3. Infrared (IR) Touch Sensors
Use IR light beams across the screen surface.
Touch interrupts the beams, identifying the position.
Used in large-format displays and kiosks.
4. Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Sensors
Use ultrasonic waves that are disturbed upon touch.
High image clarity and durability.
Common in kiosks and public terminals.
5. Optical Touch Sensors
Employ cameras or optical sensors to detect finger position.
Suitable for large interactive tables and displays.
Key Features and Advantages
✅ Intuitive User Experience – Natural input through touch and gestures
✅ Durable and Low Maintenance – Fewer mechanical parts than traditional buttons
✅ Space-Saving Designs – Slim, flat, and modern device form factors
✅ Customizable Sensitivity – Adjustable for user preferences or usage scenarios
✅ Multi-Platform Use – Applicable in consumer, industrial, automotive, and healthcare sectors
Applications of Touch Sensors
? Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, tablets, laptops, smartwatches
Touchpads and gaming controllers
? Industrial Automation
Control panels and HMI displays in harsh environments
Touchscreens for monitoring systems and machine controls
? Automotive Systems
Infotainment systems, dashboard controls, climate management interfaces
Touch-enabled steering wheels and consoles
? Healthcare & Medical Devices
Touch-controlled monitors and diagnostic equipment
Non-invasive, easy-to-clean surfaces
? Public Infrastructure
ATMs, ticketing machines, vending machines, information kiosks
? Smart Home Devices
Touch switches, thermostats, and appliance interfaces
Market Share Trends and Outlook
The global touch sensor Market Share is projected to exceed USD 20 billion by 2032, growing at a steady pace due to:
? Rising demand for smartphones and tablets
? Growth in smart appliances and IoT devices
? Adoption of touch interfaces in automotive interiors
? Transition to Industry 4.0 with advanced HMIs
Emerging Trends:
Flexible and transparent touch sensors for foldable screens
Ultrasonic and haptic feedback integration
AI-enhanced gesture recognition
Self-healing and waterproof touch surfaces
Edge-touch and bezel-less design support
Leading Touch Sensor Manufacturers
Synaptics Inc.
Cypress Semiconductor (Infineon)
Texas Instruments
Microchip Technology
NXP Semiconductors
Atmel (Microchip)
3M Company
HaptX
ELKAY
SMK Corporation
Challenges
⚡ EMI Sensitivity – Touch performance can be affected by electromagnetic interference
? Gloved Input Issues – Some technologies struggle with capacitive detection through gloves
?️ Environmental Conditions – Moisture or dust can affect accuracy
? Cost vs. Performance – High-end touch systems may increase BOM cost
Conclusion
Touch sensors are revolutionizing how we interact with technology. Their seamless integration into nearly every digital interface—whether in your hand, car, home, or office—demonstrates their versatility and reliability. As demand for sleek, responsive, and intelligent interfaces grows, the innovation in touch sensing technologies will continue to expand, paving the way for more intuitive, immersive, and connected experiences.
Read More