Herbal medicinal products represent a significant and growing segment of the global healthcare landscape, deeply rooted in traditional medicine practices worldwide. Here's a comprehensive overview of their content and global presence:
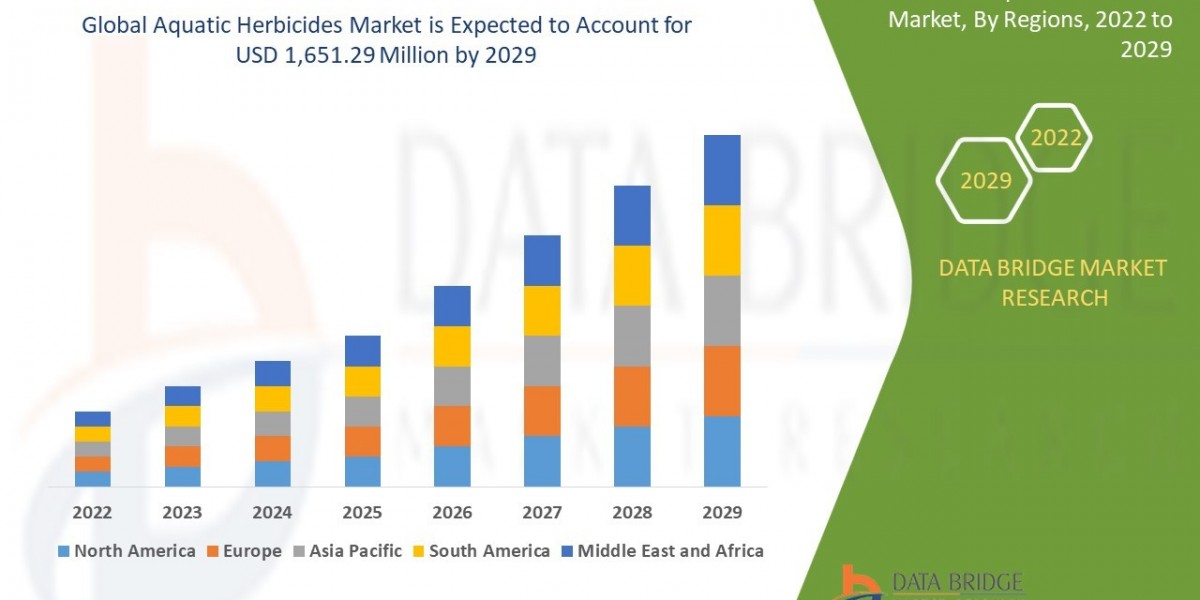
Global Market Overview:
- Driving Factors: Several factors fuel this growth, including:
- Increasing consumer interest in natural and holistic healthcare approaches.
- Rising awareness of the potential health benefits of herbal products.
- Growing preference for preventive healthcare measures.
- Perceived fewer side effects compared to synthetic drugs.
- Increasing accessibility through various distribution channels, including e-commerce.
- Aging global population and rising disposable incomes.
- Regional Variations:
- Europe: Currently holds a significant market share, attributed to a well-established pharmaceutical and medical industry and strong interest in traditional medicines like Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM).
- North America: Is experiencing the highest growth rate, driven by the legalization and acceptance of CBD products and a strong preference for organic and natural remedies.
- Asia-Pacific: Represents a large and rapidly growing market due to deep-rooted traditions in herbal medicine (Ayurveda, TCM, Kampo), increasing consumer awareness, and rising incomes.
- Africa: A significant portion of the population relies on traditional medicine, including herbal remedies, as a primary healthcare solution.
Content and Types of Herbal Medicinal Products:
Herbal medicinal products are derived from various parts of plants and come in diverse formulations:
- Source Materials: These products utilize different parts of plants, including:
- Roots: Turmeric, ginger, ashwagandha.
- Leaves: Peppermint, eucalyptus.
- Bark: Willow bark.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Elderberry.
- Seeds: Flaxseed.
- Flowers.
- Product Types: The market encompasses a wide array of products:
- Herbal Supplements: Capsules, tablets, powders containing standardized herbal extracts.
- Tinctures: Alcoholic extracts of herbs.
- Extracts: Concentrated preparations obtained using various solvents.
- Traditional Medicines: Ayurvedic, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Homeopathic, and other traditional formulations.
- Aromatherapy Products: Essential oils derived from plants.
- Syrups: Liquid formulations with herbal extracts and sweeteners.
- Oils: Herbal extracts in oil base for topical or internal use.
- Creams and Ointments: Topical preparations for skin conditions and pain relief.
- Teas: Dried herbs for infusion.
- Gummies: Chewable formulations, often for children.
- Primary Ingredients: Some globally popular ingredients include:
- Cannabidiol (CBD)
- Turmeric
- Elderberry
- Ashwagandha
- Ginseng
- Milk Thistle
- Aloe Vera
Global Regulatory Landscape:
The regulation of herbal medicinal products varies significantly across the globe:
- Developed Nations: Countries like the USA, Germany, Japan, and those in the European Union (EU) generally have more established and rigorous regulatory frameworks. In the EU, the Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products Directive (THMPD) specifically addresses the regulation of these products.
- Developing Nations: Regulatory frameworks may be weaker, leading to challenges in ensuring the safety and quality of herbal medicines.
- International Cooperation: The World Health Organization (WHO) facilitates the International Regulatory Cooperation for Herbal Medicines (IRCH), a network of regulatory authorities aimed at collaboration and sharing best practices to improve the regulation and safe use of herbal medicines. As of January 2025, IRCH had 49 member countries and regional bodies.
- Challenges in Regulation: Key barriers include a lack of research on herbal medicines, insufficient regulatory mechanisms, reluctance of traditional healers to engage with scientific communities, inadequate inspections, and limited data on safety, quality, and efficacy.
- Importance of Regulation: As the demand for herbal products grows, robust regulatory activity is crucial to address public health concerns and ensure product safety, quality, and proper labeling.
Traditional Medicine Practices and Herbal Products:
Herbal medicinal products are intrinsically linked to traditional medicine systems practiced globally:
- Widespread Use: Traditional medicine remains a primary healthcare resource for a large percentage of the population in many developing countries. Even in industrialized nations, there's increasing interest and use of traditional and complementary medicine.
- Diverse Systems: Various traditional medicine systems worldwide utilize herbal remedies, including Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine, Unani, Siddha medicine, traditional African medicine, and many others.
- Integration with Modern Medicine: Interestingly, a significant percentage of modern pharmaceutical drugs have origins in natural products and traditional knowledge, highlighting the historical and ongoing contribution of herbal medicine to conventional medicine.
In conclusion, herbal medicinal products constitute a dynamic and expanding global market, drawing upon a rich history of traditional medicine practices. While offering potential health benefits and appealing to a growing consumer base seeking natural alternatives, the diverse regulatory landscape presents ongoing challenges in ensuring consistent safety and quality worldwide.