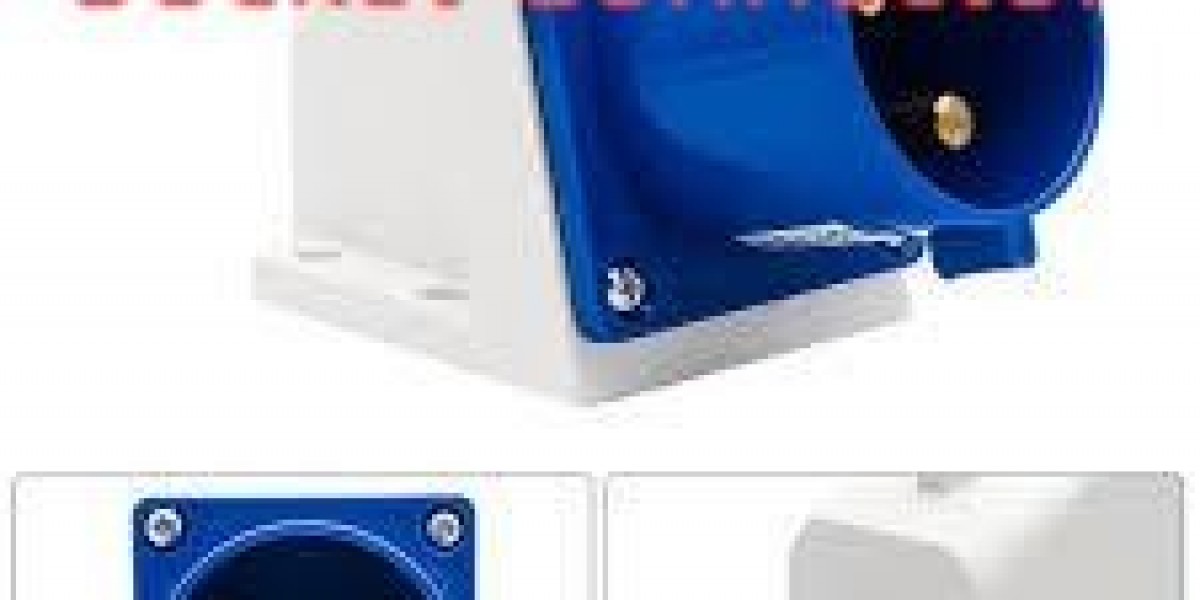
In modern manufacturing environments, the Industrial Plug Socket Connector plays a pivotal role in maintaining uninterrupted power delivery across heavy machinery and control panels. Selecting the right unit involves balancing durability, safety standards, and ease of installation. From metal-clad production lines to outdoor construction sites, these connectors must withstand dust, moisture, and mechanical stress without compromising performance or worker safety.
1. Key Design Considerations
When evaluating any power connection solution, engineers prioritize ingress protection ratings (IP65, IP67, or higher) to safeguard against water jets and particulate ingress. Equally important are the connector’s current and voltage specifications—matching them correctly prevents overheating and potential downtime. Ergonomic design features, such as color-coded housings and keyed inserts, also reduce wiring errors during routine maintenance.
2. Material and Construction
High-grade thermoplastics and die-cast aluminum alloys dominate modern connector housings. Thermoplastics offer excellent chemical resistance and lighter weight, whereas aluminum provides superior mechanical strength and heat dissipation. Internally, brass or copper alloy contacts plated with nickel or silver ensure low electrical resistance and long-term reliability, even under rapid connect/disconnect cycles.
3. Schneider Electric Solutions
Schneider Electric has long been recognized for producing connectors that meet stringent global standards. Their modular range allows for quick field upgrades, and integrated safety shutters prevent accidental contact with live parts. Furthermore, these units seamlessly integrate into broader automation architectures, supporting both standard power feeds and data communication lines without additional adapters.
4. Installation Best Practices
Proper mounting and sealing are crucial. Always use compatible gasket materials and torque the housing screws to manufacturer specifications to maintain IP integrity. Before energizing, verify correct phase sequencing and grounding continuity with a calibrated multimeter. Label each connector according to the site’s wiring diagram to simplify future troubleshooting and expansions.
5. Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Routine inspections—scheduled at least every six months—should include visual checks for housing cracks, corrosion on contacts, and cable strain relief integrity. Cleaning with non-conductive solvents extends connector life, while replacing worn seals prevents moisture ingress. Documenting each inspection and any replacements in a digital log helps predict component lifespans and budget for timely upgrades.
In applications requiring versatile and robust connections, integrating an Industrial Plug Socket Connector that aligns with both operational demands and safety codes can dramatically reduce unplanned stoppages. By following manufacturer guidelines for installation and maintenance, facilities can ensure peak performance and extend the service life of their electrical infrastructure.