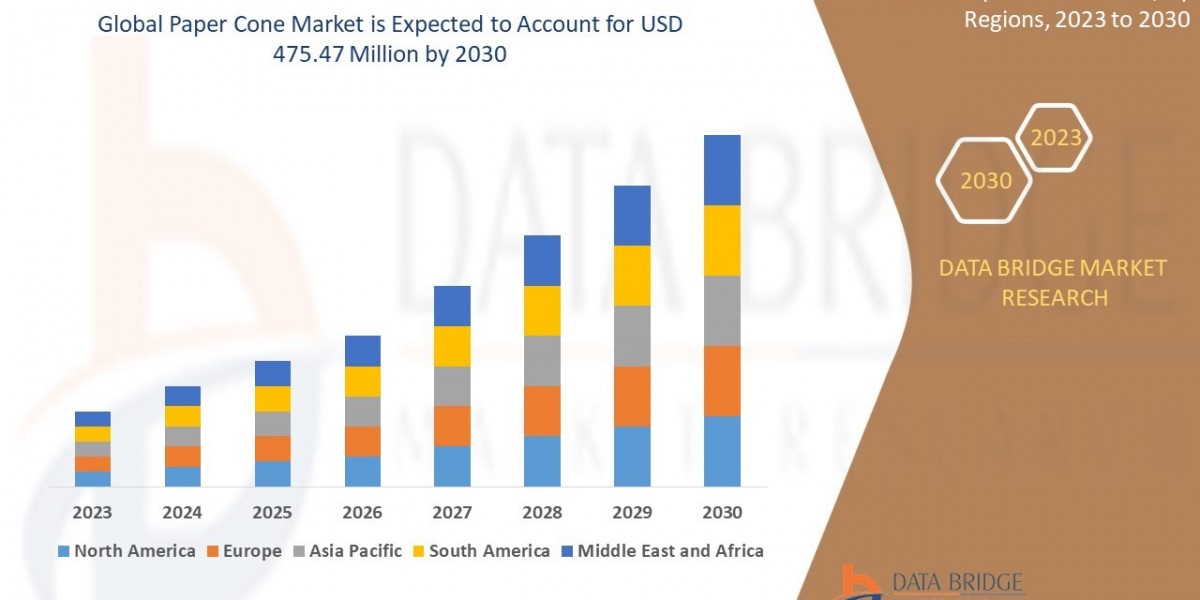
Microfinance Lending: Empowering Small Enterprises and Underserved Communities
Introduction
Microfinance lending is a powerful tool that bridges the financial gap for individuals and small businesses that are typically excluded from traditional banking systems. It plays a pivotal role in poverty alleviation and economic development by providing small loans—often referred to as microloans—to low-income individuals, particularly in developing countries. These loans enable recipients to start or expand small businesses, invest in education, or improve their homes and living standards.
What is Microfinance Lending?
Microfinance lending Market refers to the provision of financial services, especially small loans, to individuals or groups who do not have access to conventional banking. It includes not just credit, but also savings, insurance, and money transfers. The core idea is to empower economically disadvantaged people by giving them access to the financial tools they need to build sustainable livelihoods.
Typically, loan amounts range from as little as $50 to a few thousand dollars, depending on the borrower’s need and repayment capacity. The loans are usually unsecured and are provided through microfinance institutions (MFIs), non-governmental organizations (NGOs), cooperatives, and even some mainstream banks.
Key Features of Microfinance Lending
Small Loan Amounts
Microfinance loans are much smaller than traditional loans and are tailored to meet the specific needs of low-income borrowers.Group Lending Model
Many microfinance institutions adopt a group lending approach, where a group of borrowers is jointly responsible for loan repayment. This creates peer pressure and mutual accountability, improving repayment rates.Collateral-Free Lending
Unlike traditional banks, microfinance loans usually do not require collateral, making them accessible to individuals without assets.Flexible Repayment Terms
Repayment schedules are often customized to suit the borrower’s cash flow, such as weekly or biweekly payments.Focus on Women Empowerment
A significant percentage of microfinance loans are extended to women, fostering gender equality and empowering women to become financially independent.
Benefits of Microfinance Lending
Poverty Reduction: Microfinance helps people generate income and lift themselves out of poverty through entrepreneurship.
Employment Generation: By funding micro-enterprises, microfinance contributes to local job creation.
Financial Inclusion: It brings the unbanked population into the formal financial system.
Social Empowerment: Particularly for women, microfinance improves social status and household decision-making power.
Community Development: When more people have access to finance, local economies grow and communities thrive.
Challenges in Microfinance Lending
High Interest Rates: Due to administrative costs and risks, microloans often come with higher interest rates than traditional loans.
Over-Indebtedness: Some borrowers take multiple loans from different lenders, leading to repayment challenges.
Sustainability of MFIs: Many microfinance institutions rely on donor funding and face sustainability issues.
Regulatory Hurdles: Inconsistent regulations across countries can create operational complexities for MFIs.
Impact Measurement: It can be difficult to measure the long-term impact of microfinance on poverty alleviation accurately.
The Future of Microfinance Lending
The microfinance sector is evolving with the help of digital technology. Mobile banking, digital lending platforms, and fintech solutions are enabling faster loan disbursals, lower operational costs, and improved customer outreach. Governments and international organizations are also playing a larger role in supporting the sector through favorable policies and funding support.
Furthermore, a growing focus on social impact investing is bringing new capital into the sector, allowing MFIs to scale their operations and reach more underserved populations.
Conclusion
Microfinance lending continues to be a transformative force for millions of people worldwide. By providing access to credit and financial services, it fosters entrepreneurship, promotes financial inclusion, and uplifts communities. While there are challenges to be addressed, the ongoing innovation and policy support make microfinance a promising tool for inclusive economic development.
Related Report -
Blockchain in Insurance Market